The COVID-19 pandemic has been a major global health crisis. It’s caused by the SARS-CoV-2 virus, which has spread fast around the world. This has put a lot of pressure on healthcare systems and changed life for millions.
At the center of this pandemic is the SARS-CoV-2 virus. It’s very contagious and can spread quickly. This has made it a big challenge for doctors and leaders everywhere.
Key Takeaways
- COVID-19 is a global health crisis caused by the SARS-CoV-2 virus, a highly contagious novel coronavirus.
- The COVID-19 pandemic has posed significant challenges to healthcare systems and disrupted daily life for millions of people worldwide.
- Understanding the nature and characteristics of the SARS-CoV-2 virus is crucial in navigating the COVID-19 pandemic effectively.
- The rapid transmission and potential for severe illness associated with COVID-19 have made it a formidable challenge for healthcare professionals and policymakers.
- Staying informed about the latest developments and taking appropriate preventive measures are essential in addressing the COVID-19 pandemic.
What is the Covid-19?
Covid-19, also known as the novel coronavirus, is a highly contagious respiratory illness. It is caused by the SARS-CoV-2 virus. This virus has spread globally, affecting public health and economies worldwide. Knowing how Covid-19 works is key to fighting this health crisis.
Understanding SARS-CoV-2 Structure
The SARS-CoV-2 virus is part of the coronavirus family. It has a unique crown-like shape. It has genetic material wrapped in a lipid envelope and spike proteins on its surface.
These spike proteins help the virus attach to and infect human cells.
How Coronaviruses Work
Coronaviruses, like SARS-CoV-2, take over host cells to replicate and spread. The virus’s RNA genetic material enters the host cell. It tells the cell to make more viral particles.
This leads to the virus multiplying quickly in the body. This can make the illness worse.
| Characteristic | Description |
|---|---|
| Genetic Material | Single-stranded RNA |
| Envelope | Lipid bilayer |
| Spike Proteins | Protrude from the surface and facilitate cell entry |
| Replication Mechanism | Hijacks host cell machinery to produce more viral particles |
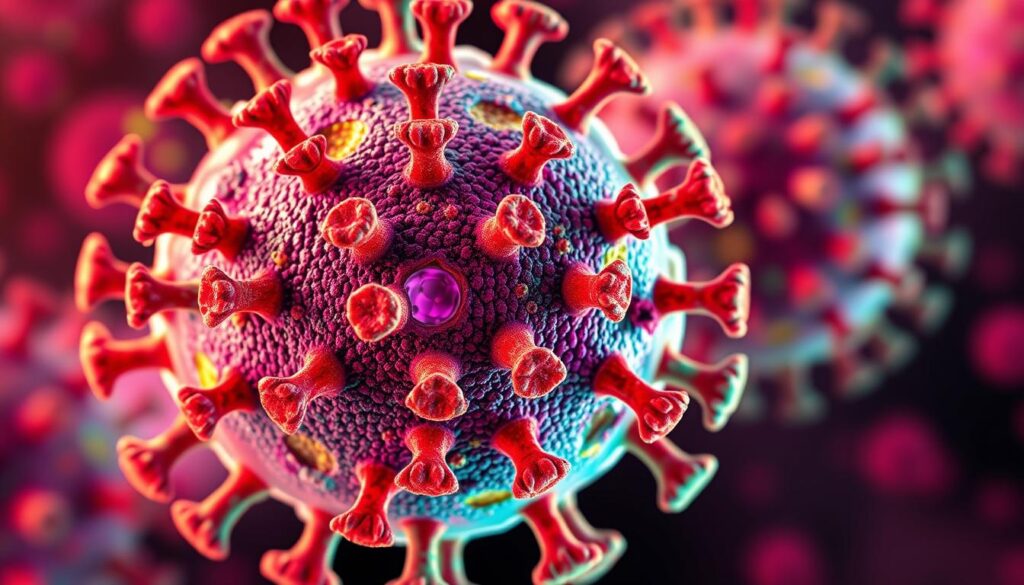
“The SARS-CoV-2 virus is a formidable adversary, but understanding its structure and replication mechanisms is crucial to developing effective strategies to combat this pandemic.”
The Origins and Emergence of Covid-19 in Wuhan
The coronavirus origins have been a focus of scientists since the Wuhan outbreak started. The exact source of the SARS-CoV-2 virus is still being studied. Many think it likely came from an animal to humans through zoonotic transmission.
One theory is that the virus first appeared in the Huanan Seafood Wholesale Market in Wuhan, China. This market sold live animals, including exotic ones. It was a place where the virus could have jumped from animals to humans.
“The Huanan Seafood Wholesale Market in Wuhan was the first known epicenter of the Covid-19 outbreak, but the exact animal source of the virus remains a mystery.”
Early reports showed many Covid-19 cases were linked to the Wuhan market. This led researchers to believe it was where the first human transmission happened. But, the exact animal that carried the virus and passed it to humans is still being looked into.

As scientists keep working to understand the coronavirus origins, knowing how Covid-19 first spread in Wuhan is key. This knowledge will help us prepare better for the future and stop similar outbreaks.
How Covid-19 Spreads: Transmission Methods and Risk Factors
It’s important to know how Covid-19 spreads to stop it. The main ways it spreads are through droplet transmission, surface contamination, and airborne spread. Let’s look at each method closely.
Droplet Transmission
The virus mainly spreads through droplets when someone coughs, sneezes, or talks. These droplets can hit the faces of people nearby, causing infection. Places where people are close together, like parties or crowded areas, are riskier.
Surface Contamination
The virus can also spread through contaminated surfaces, or fomites. When someone with the virus touches a surface, the virus stays there. If others touch that surface, they can get infected. Washing hands often and cleaning high-touch areas helps stop this spread.
Airborne Spread
Studies show Covid-19 can spread through airborne transmission, especially in places with bad air flow. Tiny droplets, or aerosols, can stay in the air and be breathed in by others. Good air flow and filters can lower this risk.
Knowing how Covid-19 spreads helps us take steps to protect ourselves and others. We can all play a part in stopping its spread.
Identifying Common Covid-19 Symptoms and Warning Signs
The Covid-19 pandemic keeps changing, and knowing the symptoms is key. The main signs are fever, cough, and shortness of breath. But, the virus can show up in many other ways too.
Some less common symptoms include:
- Fatigue
- Muscle or body aches
- Headache
- New loss of taste or smell
- Sore throat
- Congestion or runny nose
- Nausea or vomiting
- Diarrhea
How bad Covid-19 symptoms are can vary a lot. Some people might not feel anything, while others could get very sick and need help right away.
Warning signs that mean you need to go to the emergency room include:
- Difficulty breathing or shortness of breath
- Persistent pain or pressure in the chest
- New confusion or inability to arouse
- Bluish lips or face
If you or someone you know has these serious symptoms, get help fast. Quick action can make a big difference in how well someone recovers.
Knowing about Covid-19 symptoms helps us all stay safe. It’s important to stay informed and watch out for each other during this tough time.
Timeline of the Global Pandemic Development
The coronavirus pandemic has changed the world, leaving a lasting impact on our lives. It started with early outbreaks, spread globally, and had major waves. These phases have shaped our understanding of the crisis.
Early Outbreak Phases
The first cases of the coronavirus, now known as SARS-CoV-2, were in Wuhan, China, in late 2019. The Chinese government quickly locked down areas and took health measures. But, the virus spread internationally, and by March 2020, it was a global pandemic, as declared by the World Health Organization.
Global Spread Patterns
The virus spread fast, touching every continent. At first, Europe and North America were hit hard. But soon, it reached every corner of the world. The virus’s impact varied due to different healthcare systems and government responses.
Major Pandemic Waves
- The first big wave hit in the spring of 2020, overwhelming healthcare systems worldwide.
- After public health measures and vaccines, the pandemic seemed to slow down. But, new waves, like the delta and omicron variants, brought new challenges.
- These waves show the pandemic is ongoing. We must keep working to stop the virus and its variants.
The story of the coronavirus pandemic is complex and still unfolding. It’s vital to understand this timeline to face future challenges. It helps us prepare for a stronger future.
Covid-19 Testing Methods and Accuracy
As the Covid-19 pandemic keeps changing, it’s key to know the different testing methods. This helps in accurate diagnosis and managing the virus. The main methods are PCR tests, rapid antigen tests, and antibody testing.
PCR Tests: The Gold Standard
PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) tests are the top choice for finding active Covid-19 infections. They look for the virus’s genetic material, giving a precise diagnosis. These tests are done in labs and can spot the virus even in people who don’t show symptoms.
Rapid Antigen Tests: Convenience at a Cost
Rapid antigen tests are quicker and easier than PCR tests. They find proteins from the SARS-CoV-2 virus and give results in minutes. Though not as accurate as PCR tests, they’re useful for quick screenings in high-risk places.
Antibody Testing: Assessing Past Exposure
Antibody tests, or serological tests, check for the body’s immune response to the virus, not the virus itself. They show if someone has had Covid-19, even if they didn’t show symptoms. These tests are great for studying past infections and understanding how widespread they were.
| Testing Method | Accuracy | Turnaround Time | Suitable Use |
|---|---|---|---|
| PCR Tests | High (>95% sensitivity) | 1-2 days | Diagnosing active infections |
| Rapid Antigen Tests | Moderate (70-80% sensitivity) | 15-30 minutes | Screening for active infections in high-risk settings |
| Antibody Tests | Moderate (80-90% sensitivity) | 1-2 days | Assessing past exposure and prevalence studies |
Knowing the good and bad of each Covid-19 testing method is key. It helps in choosing the right testing strategy and understanding the results.
“The key to controlling the Covid-19 pandemic lies in widespread and accessible testing, which allows us to identify infected individuals and implement effective public health measures.”
Preventive Measures and Safety Protocols
In the fight against the covid-19 pandemic, following key steps is vital. These include wearing personal protection equipment and practicing good hygiene. These actions help lower the risk of getting sick and keep everyone safe.
Personal Protection Equipment
Health experts say face masks are a top way to stop covid-19. They help block the spread of droplets that carry the virus. Wearing gloves and face shields can also add extra protection in risky places.
Social Distancing Guidelines
Keeping a safe distance from others is key. This means staying at least 6 feet (2 meters) away. It helps prevent the spread of the virus by reducing contact with droplets and aerosols. Following these rules in places like stores and public transport is very important.
Hygiene Practices
Keeping hands clean is a big part of fighting covid-19. Washing hands well with soap and water or using hand sanitizers can remove the virus. It’s also important to cover your mouth when you cough or sneeze and not touch your face.
| Preventive Measure | Effectiveness | Recommendation |
|---|---|---|
| Face Masks | High | Wear properly fitted face coverings in public settings |
| Social Distancing | High | Maintain at least 6 feet (2 meters) of distance from others |
| Hand Hygiene | High | Frequent handwashing with soap and water or use of alcohol-based sanitizers |
By taking these steps, we can all help stop the virus. This protects us and our communities.
Covid-19 Variants and Mutations
The SARS-CoV-2 virus has shown its ability to change and adapt during the pandemic. It has led to many variants, each with its own traits and effects. These changes are a big worry for health experts.
The Delta variant is a major concern. It was first found in India in late 2020. It spread fast, causing more cases and hospitalizations. Delta is 60% more contagious than the original virus, making it hard to control the pandemic.
The Omicron variant has also caused a lot of concern. It is believed to be even more contagious than Delta. It can also get past some of the protection from vaccines, raising worries about vaccine effectiveness.
| Variant | Characteristics | Potential Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Delta |
|
|
| Omicron |
|
|
New variants of SARS-CoV-2 keep appearing. To fight these changes, we need to keep watching the virus, sequence its genes, and update vaccines. This is key to managing the pandemic.
Vaccines Development and Distribution
The quick creation of Covid-19 vaccines is a huge scientific win. It shows how fast we can work when we need to. These vaccines, like mRNA, viral vector, and protein subunit, work well in tests. They’ve been approved for emergency use worldwide.
Types of Covid-19 Vaccines
The main Covid-19 vaccines fall into three types:
- mRNA Vaccines – These, like Pfizer-BioNTech and Moderna, teach our cells to make a harmless virus piece. This piece is the virus’s spike protein, which starts an immune response.
- Viral Vector Vaccines – AstraZeneca and Johnson & Johnson use a safe virus to carry genetic material. This material codes for the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein, boosting our immune system.
- Protein Subunit Vaccines – Novavax is an example. It has purified virus pieces, which our immune system sees as foreign. This leads to an immune response.
Global Vaccination Efforts
Getting Covid-19 vaccines out has been a huge task. Countries are racing to get doses and vaccinate people. Rich countries have made good progress, but it’s not even for everyone else.
| Region | Vaccination Rate (% of population) |
|---|---|
| North America | 65% |
| Europe | 59% |
| Asia | 47% |
| Latin America and the Caribbean | 41% |
| Africa | 17% |
Getting vaccines to everyone is still a big challenge. But, as more people get vaccinated, hope grows. We’re all working to beat the Covid-19 pandemic together.
Long-term Health Effects of Covid-19
The world is still dealing with the Covid-19 pandemic. A big worry is the long-term health effects of the virus. These effects, known as “long Covid” or post-acute sequelae, can really affect someone’s life and health.
One common long-term effect is chronic fatigue. People say they feel extremely tired, even after they’ve gotten better. This makes it hard for them to do everyday things.
- Neurological issues, like brain fog and mood problems, are also seen in long Covid patients.
- Respiratory issues, like coughing and shortness of breath, can last for months.
- Cardiovascular problems, like heart inflammation, are also linked to long Covid.
Scientists are working hard to understand these long-term effects. They want to find ways to help people manage these issues. It’s important for healthcare and policymakers to support those dealing with these effects.
“The long-term health effects of Covid-19 are still being actively studied, but it’s clear that the virus can have a profound and lasting impact on an individual’s well-being. Addressing these challenges will require a collaborative and compassionate approach from the medical community and society as a whole.”
Global Economic and Social Impact
The Covid-19 pandemic has deeply affected the world’s economy and social structure. Healthcare systems worldwide have been overwhelmed, leading to job losses, business closures, and supply chain disruptions.
Healthcare Systems Impact
Hospitals globally are facing a huge challenge due to the pandemic. They are short on medical equipment, beds, and staff. This has delayed or canceled many medical procedures and disrupted regular healthcare services.
Economic Consequences
The pandemic’s economic impact has been severe. Lockdowns and travel restrictions have forced many businesses to close. This has led to millions of job losses and a significant downturn in the global economy.
It has also caused shortages of essential goods and raw materials. This has led to higher prices, making things harder for people and businesses.
“The economic damage caused by the pandemic will be felt for years to come, as businesses struggle to recover and governments work to stimulate economic growth.”
The pandemic has also changed how we interact with each other. Social distancing and lockdowns have increased isolation and mental health issues. They have also changed how we work, learn, and socialize.
As the pandemic continues, its economic and social effects will last. Governments, businesses, and individuals must work together. They need to build a more resilient and fair future.
Current Status and Future Outlook
The world is still dealing with the COVID-19 pandemic’s challenges. We’ve made big steps in fighting the virus, thanks to vaccines and better understanding. Yet, the future is uncertain, with both hopes and worries about moving past the pandemic.
The pandemic showed us how important strong health systems and global teamwork are. Now, we need to focus on recovering from the pandemic and getting ready for the future. Governments, health systems, and global groups are working together to lessen COVID-19’s long-term effects and prepare for future health threats.
There’s a glimmer of hope that we’re moving towards a new normal. As the virus changes, we’re learning to live with it as an endemic disease. By supporting research, improving healthcare, and working together globally, we can face future challenges and build a stronger future.















Leave a Reply